What is Dark Energy? Inside our accelerating, expanding Universe
FEB 05, 2024. Chelsea Gohd.
What Exactly is Dark Energy?
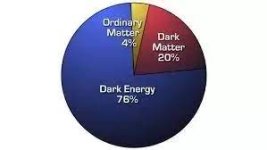
Right now, dark energy is just the name that astronomers gave to the mysterious "something"
that is causing the universe to expand at an accelerated rate.
Dark energy has been described by some as having the effect of a negative pressure
that is pushing space outward. However, we don't know if dark energy has the effect
of any type of force at all. There are many ideas floating around about what dark energy
could possibly be. Here are four leading explanations for dark energy.
Keep in mind that it's possible it's something else entirely.
Vacuum Energy:
Some scientists think that dark energy is a fundamental, ever-present background energy
in space known as vacuum energy, which could be equal to the cosmological constant,
a mathematical term in the equations of Einstein's theory of general relativity.
Originally, the constant existed to counterbalance gravity, resulting in a static universe.
But when Hubble confirmed that the universe was actually expanding,
Einstein removed the constant, calling it “my biggest blunder,” according to physicist George Gamow.
. . . -----
By Chelsea Gohd
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory

 science.nasa.gov
------
science.nasa.gov
------
FEB 05, 2024. Chelsea Gohd.
What Exactly is Dark Energy?
Right now, dark energy is just the name that astronomers gave to the mysterious "something"
that is causing the universe to expand at an accelerated rate.
Dark energy has been described by some as having the effect of a negative pressure
that is pushing space outward. However, we don't know if dark energy has the effect
of any type of force at all. There are many ideas floating around about what dark energy
could possibly be. Here are four leading explanations for dark energy.
Keep in mind that it's possible it's something else entirely.
Vacuum Energy:
Some scientists think that dark energy is a fundamental, ever-present background energy
in space known as vacuum energy, which could be equal to the cosmological constant,
a mathematical term in the equations of Einstein's theory of general relativity.
Originally, the constant existed to counterbalance gravity, resulting in a static universe.
But when Hubble confirmed that the universe was actually expanding,
Einstein removed the constant, calling it “my biggest blunder,” according to physicist George Gamow.
. . . -----
By Chelsea Gohd
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory

What is Dark Energy? Inside our accelerating, expanding Universe - NASA Science
Some 13.8 billion years ago, the universe began with a rapid expansion we call the big bang. After this initial expansion, which lasted a fraction of a second, gravity started to slow the universe down. But the cosmos wouldn’t stay this way. Nine billion years after the universe began, its...